| [1] 田卫东,温海林,汪明祖.一种可任意调节角度的牙种植体系统:中国,201210587180.9[P].2013-05-01
[2] Branemark PI,Zarb GA,Albrektsson T.Tissue-Integrated Prostheses: Osseointegration in Clinical Dentistry.Chicago: Quintessence Publishing Co.Inc. 1985.
[3] Covani U1,Ricci M,Bozzolo G.Analysis of the pattern of the alveolar ridge remodeling following single tooth extraction.Clin Oral Implants Res.2011; 22(8):820-825.
[4] Kim DG,Huja SS,Tee BC,et al.Bone ingrowth and initial stability of titanium and porous tantalum dental implants: a pilot canine study.Implant Dent.2013;22(4):399-405.
[5] Ivanov SI,Muraev AA,Fomin MI,et al.Dental implants in complex oral rehabilitation in patients with class III occlusion and partial teeth loss.Stomatologiia (Mosk).2013;92(3):38-42.
[6] Ugurlu F,Y?ld?z C,Sener BC,et al.Rehabilitation of posterior maxilla with zygomatic and dental implant after tumor resection: a case report.Case Rep Dent. 2013;2013:930345.
[7] Revah A,Rehany A,Zalkind M,et al.The tilted posterior tooth. Part III: Abutment for a fixed partial denture.J Prosthet Dent. 1985;54(3):325-330.
[8] Celik G,Uludag B.Photoelastic stress analysis of various retention mechanisms on 3- implant-retained mandibular over dentures.J Prosthet Dent.2007;97(4):229-235.
[9] Tada S,Stegaroiu R,Kitamura E,et al.Influence of implant design and bone quality on stress/strain distribution in bone a-round implants.J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2003;18(3): 357-368.
[10] Juodzbalys G,Sapragoniene M,Wennerberg A,et al.Titanium dental implant surface micromorphology optimization.J Oral Implantol.2007;33(4):177-185.
[11] 李鹏,梁瑞,申龙朵,等.应用Mimics和ANSYS软件建立下颌骨三维有限元模型的方法学研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志, 2012,28(6): 709-713.
[12] 谢敏理,和丽,许纪倩.Pro/E二次开发实现自动装配的一种方法[J].现代机械,2006,33(1):46-48.
[13] Tada S,Stegaroiu R,Kitamura E,et al.Influence of implant design and bone quality on stress /strain distribution in bone around implants: a 3-dimensional finite element analysisInt J Oral Maxillofac Implants.2003;18(3):357-368.
[14] Meyer U,Vollmer D,Christoph B,et al.Bone loading pattern around implants in average and atrophic edentulous maxillae: a finite-element analysis.J Cranio-Maxillofac Surg. 2001; 29(2):100-105.
[15] 高飞,张恩维,魏世成,等.种植体螺纹结构及接触面静力和疲劳分析[J].中国组织工程与临床康复,2010,14(30):5531-5534.
[16] Meijer HJ,Kuiper JH,Starmans FJ,et al.Stress distribution around the dental implants. Influence of superstructure, length of implants, and height of mandible. J Prosthet Dent. 1992;68(1):96-102.
[17] Kao HC,Gung YW,Chung TF,et al.The influence of abutment angulation on micromotion level for immediately loaded dental implants: a 3-D finite element analysis.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.2008;23(4):623-630.
[18] 谭荣,施斌.封闭介质对粘结固定型种植义齿应力分布的影响[J].口腔医学研究,2004,20(1):22-25.
[19] 冯士刚,艾芊.带精英策略的快速非支配排序遗传算法在多目标无功优化中的应用[J].电工技术学报,2007,22(12):146-151.
[20] 杨周妮,吴作伟,雷铁安.ANSYS优化方法与遗传算法在结构优化方面的比较[J].自动化技术与应用,2004,23(7):4-6.
[21] 范德礼,郑世杰.基于遗传算法和结构优化的多裂纹梁损伤识别[J].江苏航空,2011,31(s1):49-53.
[22] Adell R,Eriksson B,Lekholm U,et al.Long-term follow up study of osseointegrated implants in the treatment of totally eden-tulous jaws.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1990;5(4): 347-359.
[23] Osman RB,Elkhadem AH,Ma S,et al.Titanium versus zirconia implants supporting maxillary overdentures: three-dimensional finite element analysis.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.2013;28(5):198-208.
[24] I-Chiang C,Shyh-Yuan L,Ming-Chang W,et al.Finite element modelling of implant designs and cortical bone thickness on stress distribution in maxillary type IV bone.Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin.2014;17(5):516-526.
[25] Tada S,Stegaroiu R,Kitamura E,et al.Influence of implant design and bone quality on stress/strain distribution in bone around implants: a 3-dimensional finite element analysis.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.2003;18(3):357-368.
[26] 沈庆赋,蔡永刚,韩素珍.种植体折断的预防及处理[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2005,21(11):674-675.
[27] 袁会诚,马辅安,刘康民.种植体颈部锥度和末端倒角的生物力学优化分析[J].口腔医学研究,2007,23(5):516-518.
[28] 马清亮,胡昌华,杨青.一种用于多目标优化的混合遗传算法[J].系统仿真学报,2004,16(5):1038-1040.
[29] 王雅莉,伞冰冰,朱召泉.基于遗传算法的飞艇结构多目标优化[J].四川建筑科学研究,2014,40(1):39-43.
[30] 于海莲,王永泉,陈花玲,等.响应面模型与多目标遗传算法相结合的机床立柱参数优化[J].西安交通大学学报,2012,46(11):80-85.
[31] Zarone F,Apicella A,Nicolais L,et al.Mandibular flexure and stress build-up in mandibular full-arch fixed prostheses supported by osseointegrated implants.Clin Oral Implants Res.2003;14:103-114.
[32] 梁瑞,郭维华,温海林,等.12 种不同几何形状的种植体的生物力学分析[J].四川大学学报:工程科学版,2012,55(s2):60-63. |
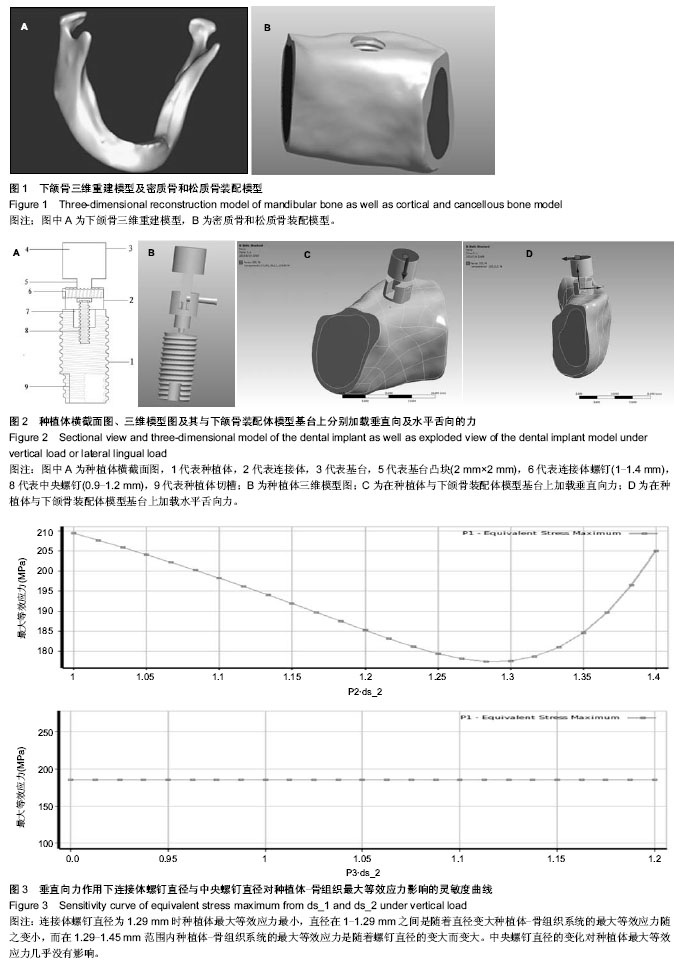

.jpg)
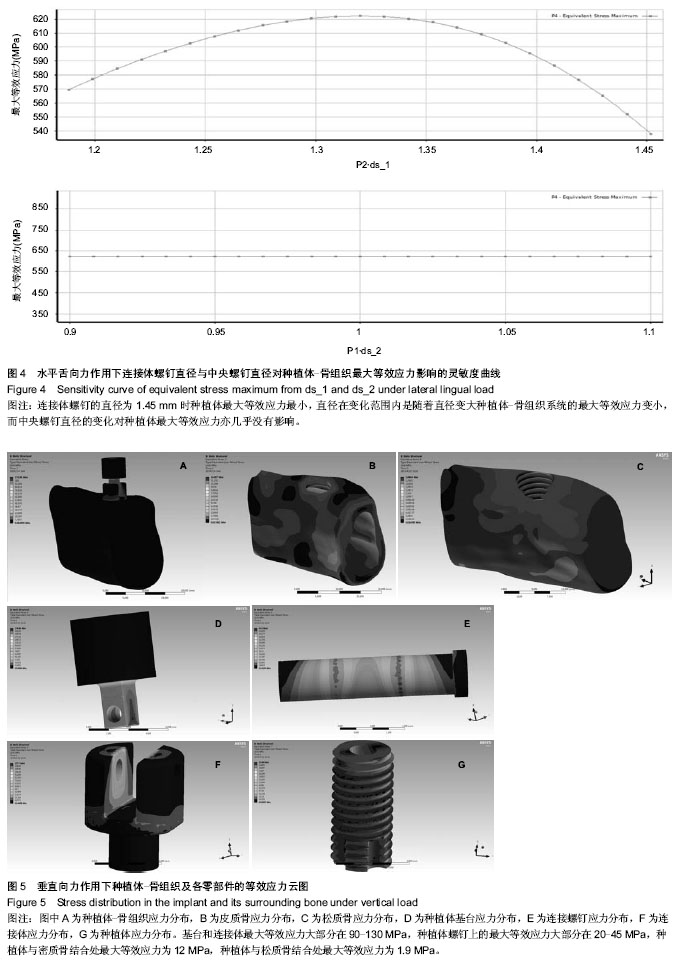
.jpg)